Imagine searching for a vacation destination and instantly getting results that understand the words you typed and the context of your query, just like a human being.
Instead of displaying links to travel agencies, this search engine might suggest hidden gems and local experiences that match your preferences.
This is what AI search promises.
Traditional search engines have served us well for decades, relying on algorithms that scan and rank web pages based on keywords, relevance, and authority.
But as technology has evolved, so too have our expectations for how information should be delivered. AI is set to change how we get answers by integrating machine learning, natural language processing, and even predictive analytics.
Keep reading to learn more about AI search, what sets it apart from traditional search, and how it can change the future of SEO as we know it.
What is AI Search?
AI search is a new search technology that uses artificial intelligence to deliver a faster, more personalized, and user-friendly search experience.
Unlike traditional search engines, AI search can understand natural language, determine what you mean, and even predict what you need next.
Some examples of these hyper-intelligent search engines are Perplexity AI, Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), ChatGPT, and Microsoft Bing (AI-powered GPT-4).
Let’s say you’re searching for “best pizza places in New York.” A traditional search engine might return a list of websites that highlight New York’s popular pizza havens alongside a couple of sponsored ads.
But AI can go a step further.
It can recognize that you’re likely looking for places with great reviews or pizza spots that cater to dietary restrictions. It considers context, like location, time of day, or even your previous search history, and refines the results to suit your preferences.
How Does AI Search Work?
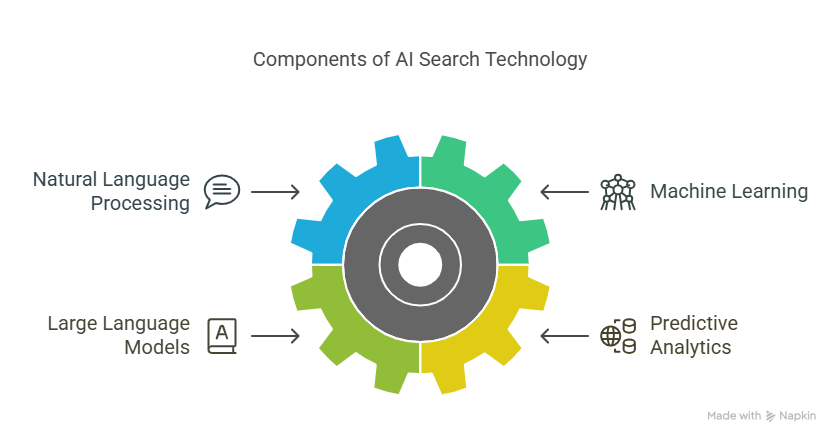
AI search is driven by advanced technologies like natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and large language models (LLMs). These help it to understand context, anticipate user intent, and provide highly relevant results.
Here’s a closer look at how these technologies work:
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) is one of the key technologies behind AI search. It helps machines understand and process human language, allowing users to ask questions as if they were talking to a real person. It drives:
- Conversational search: Understanding long, complex queries.
- Semantic search: Analyzing the meaning behind words rather than just matching keywords.
- Sentiment analysis: Detecting emotional tone in reviews or feedback.
Instead of searching for exact phrases or keywords, you can use natural, conversational queries like, “What’s the best time to visit Paris?” or “Is there a spot in Brooklyn that serves gluten-free pizza?”
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning is a form of artificial intelligence that helps search engines learn from data, identify patterns, and improve results over time, without explicit programming. It empowers AI search by analyzing user queries, understanding intent, and delivering results based on relevance.
Through continuous learning, ML enhances autocomplete suggestions, refines semantic search, and personalizes responses, making it more accurate and intuitive.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs, like OpenAI’s GPT-4 or Google’s Gemini, are trained on massive amounts of text data that help AI search engines understand natural language. This is one of the reasons ChatGPT is so good at
- Processing complete questions instead of just keywords.
- Generating summaries or direct answers.
- Converting speech to text and vice versa.
- And understanding the context of queries.
So, when you search for something like “Why do cats knead?” an AI-powered search engine can generate a fresh, detailed explanation rather than just listing web pages.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics in AI search means search engines can anticipate your queries and generate answers, even before you’ve fully typed out your request. This feature relies on machine learning models that analyze past search patterns, real-time data, and your behavior to predict what you’re looking for.
For instance, I told ChatGPT to recommend US schools still accepting applications in 2026, and it asked if I needed help choosing a program:
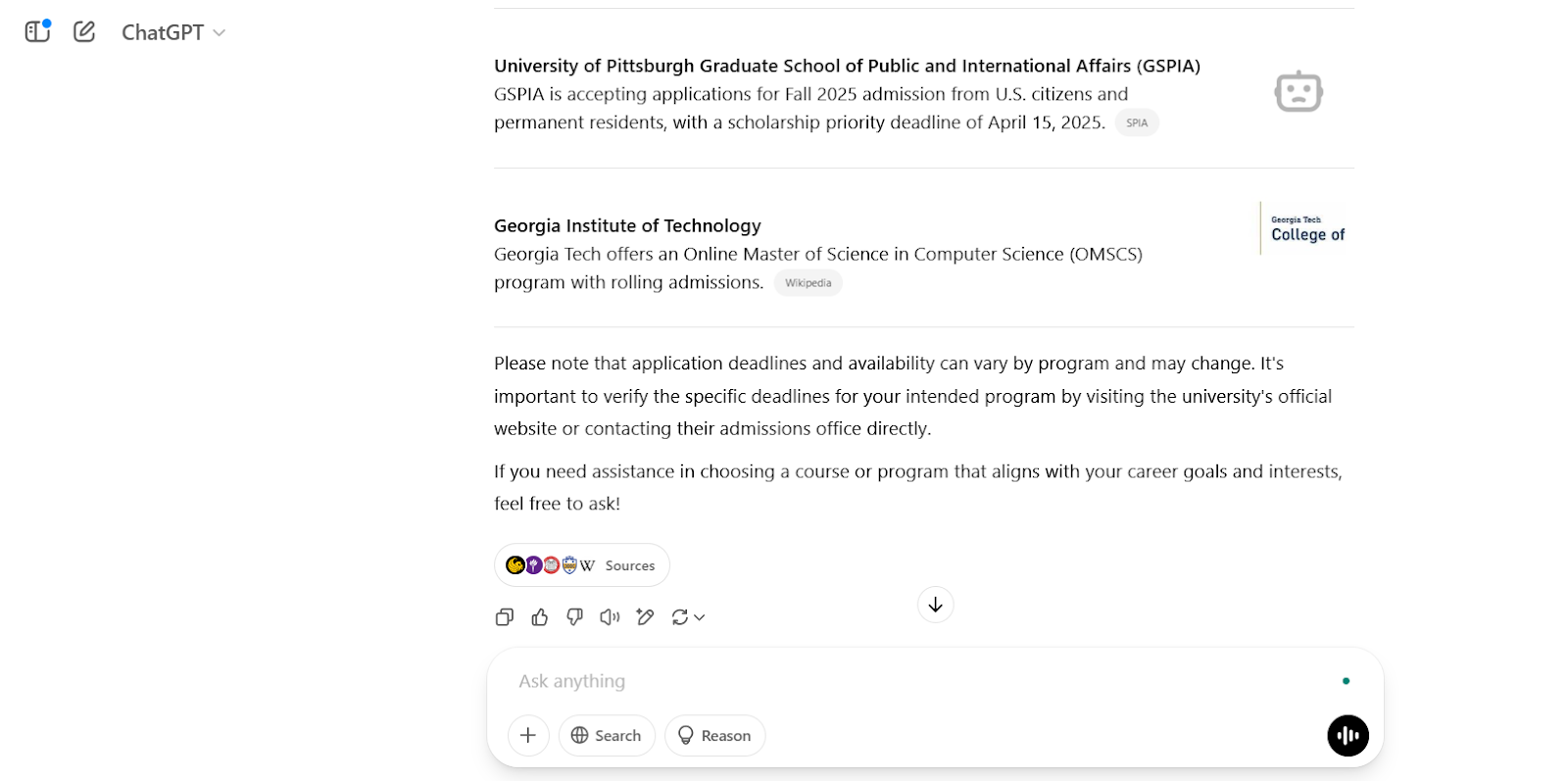
Other examples of this feature in action are autocomplete suggestions, AI-generated summaries, and instant answers in search results.
What is the Difference Between Traditional Search and AI Search?
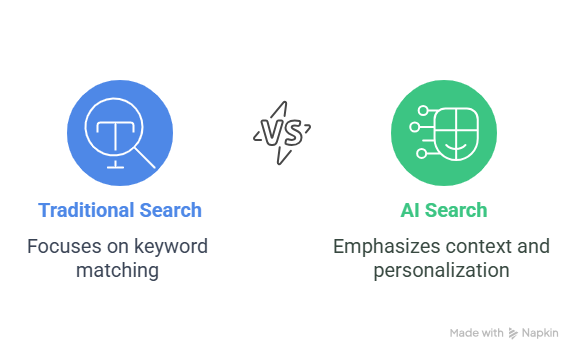
Now that we understand how AI search functions, let’s see how it stacks up against traditional search engines like Google.
Traditional Search: Keyword Matching
Traditional search engines, like Google, work by matching the words you type with the content they’ve already indexed from across the web. Think of it as a giant, algorithm-powered library.
Since 1998, Google’s mission has been to “organize the world’s information and make it more universally accessible and useful.” To do that, it uses complex formulas to weigh things like keyword relevance, backlinks, and a site’s overall authority and trustworthiness.
So, the results you see aren’t just random—they’re ranked based on what the algorithm thinks is the most reliable and relevant match for your query.
AI Search: Context, Intent Understanding, and Personalization
AI search, on the other hand, moves beyond simple keyword matching. Unlike Google, which works like a library, searching with AI is like asking an exceptionally knowledgeable friend for answers.
It understands the meaning behind your search and factors in context, intent, and even the conversation itself. Instead of relying solely on keywords, AI considers a variety of signals like user behavior, location, and past searches to deliver more accurate results. In other words, it’s all about understanding the “why” behind the search, not just the “what.”
This represents a significant shift in search technology:
- Traditional search engines are reactive: They provide results based on what they’ve already indexed and ranked.
- AI search engines are proactive: They anticipate user needs and adjust their responses accordingly, creating a more user-centered search experience.
The Pros of AI Search
In 2023, 13 million adults in the US alone used generative AI search as their primary online search tool. Those numbers are projected to reach an astounding 90 million by 2027. That’s significant traffic being taken away from traditional search models.
A lot of factors are responsible for the growing importance of AI, and here are just a few of them:
More Personalized Results
One of the most compelling benefits of AI search is its ability to deliver results tailored specifically to you.
When you search on Google, you’re interacting with content that was crafted for every Dick, Tom, and Harry. That’s why some answers can be relevant while others just miss the mark. But by learning from past searches and preferences, AI search engines can offer a more customized experience.
For example, when I searched for the key term “why am I sad” on Google, I got links to articles listing general causes of sadness and depression, like a lack of sleep, grief, and loneliness.
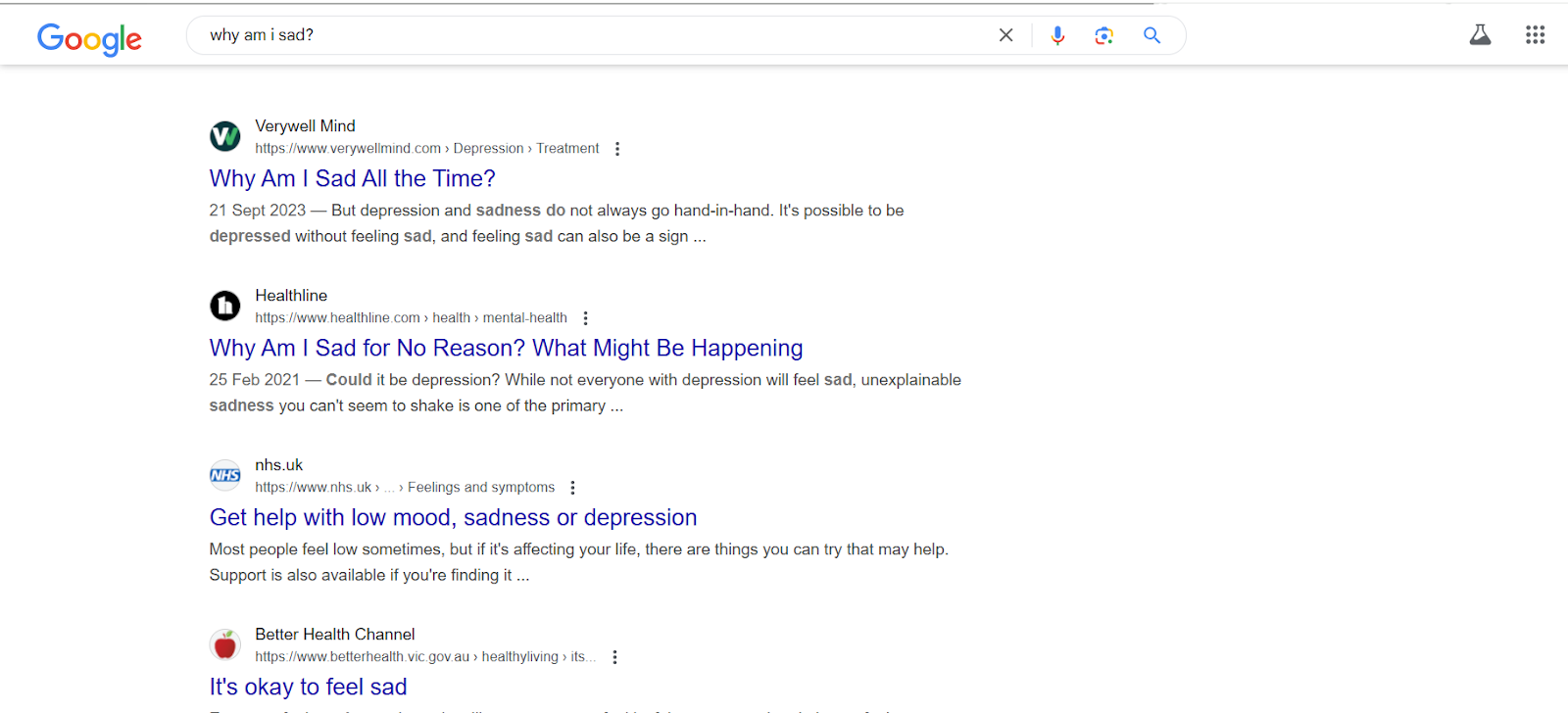
But when I took the same question to ChatGPT, it factored in potential personal causes based on our past conversations. Pretty cool if you ask me.
Enhanced User Experience
By understanding complex queries and context, AI search can provide quicker, more accurate results.
With traditional search, the process is a bit more frustrating. You type a query into Google and manually search through the ranked pages, practically jumping through hoops for some answers.
But AI removes all that extra work from the process. This means no more scrolling through ads and countless links — just precise, straightforward answers to your questions.
So, whether you’re looking for a specific restaurant or trying to solve a complex technical problem, AI can narrow your options by presenting only the most relevant information.
Natural Language Queries
Have you ever had to rephrase your question on Google before you finally got the results you were looking for? That’s because traditional search worked on a keyword basis that matched your query with relevant pages on the web.
But with AI, things have changed. You no longer need to type in perfectly optimized search phrases. You can ask questions naturally, just like you would to a person.
AI search engines understand conversational language like “What’s the weather like in Paris next week?”, “Where can I find a gluten-free bakery near me?” or even the more casual “Can you guess why I haven’t eaten today?”
This makes search more accessible, and even a lot of fun.
Continuous Improvement
AI search systems are designed to learn from user behavior. This means that the more you interact with an AI search engine, the better it understands and predicts your needs.
It’s not just a one-time solution; it’s a system that adapts and improves as it collects more data, leading to an increasingly personalized experience.
The Cons of AI Search
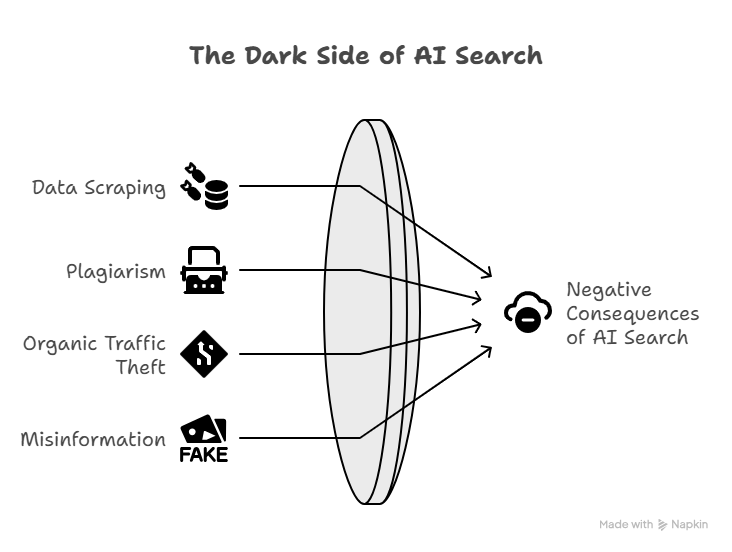
As futuristic as AI-powered search seems, there are some negative consequences to its continuous usage. Some are data scraping, plagiarism, organic traffic theft, and misinformation.
Data Privacy Concerns
AI search engines collect a lot of data to personalize results. While this can improve the search experience, it also raises privacy concerns. Many users don’t realize how much of their data is being stored, or whether that data could be misused or shared without their consent.
One popular case of AI data breach was when Target accidentally informed a man that his teenage daughter was pregnant before she had a chance to tell him herself. Yikes!
This is a clear example of how invasive AI can be. And with people constantly feeding personal data, photographs, and confidential information into generative LLMs, one wonders where all that data is stored and what kind of organizations it might be sold to.
Pro tip: When prompting AI or asking questions, avoid including confidential details about yourself, and your family. Instead, provide generic information that cannot be traced to you.
Misinformation and Hallucinations
AI models rely heavily on the quality of the data they are fed from existing information available on the internet. If the data is incomplete, biased, or inaccurate, the results will be the same.
And sometimes, AI makes stuff up, or hallucinates, just for the fun of it.
Let’s take a walk back to May 2024, when Google first released AI overviews. This initial model went viral for generating harmful results. It added gasoline to a spaghetti recipe, recommended using glue for cheesier pizzas, and eating rocks to aid digestion, all with utmost confidence!
Even with all attempts to tame misinformation on these AI models, they explicitly state that inaccurate responses are not uncommon. Here’s one of such disclaimers on ChatGPT’s main page:
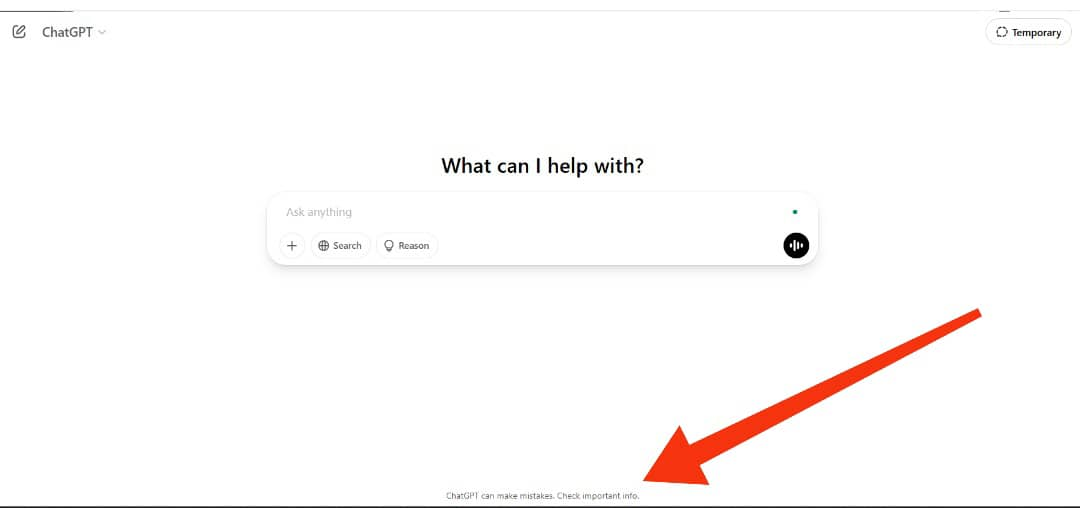
This means you’ll have to verify all of AI’s claims on authoritative sites. This begs the question: If we have to fact-check everything AI generates through traditional search, why use it at all?
The Plagiarism Problem
Picture spending hundreds of hours crafting unique articles for your audience. You’re up all night conducting research, interviewing experts, and writing something your readers will love. But then some guy just paraphrases all your hard work and takes all the credit.
Sounds familiar? Sure — because that’s what AI search engines do.
They summarize information from blogs, news sites, and forums, and profit from them.
Bloggers, journalists, and researchers spend time creating high-value content, only for AI to extract key insights and display them directly in search results — without sending any traffic back to the original sites.
In 2023, this led to the New York Times vs. OpenAI lawsuit, where the NYT accused the AI model of exploiting its publications.
These blatant acts of plagiarism could lead to a decline in independent research, creativity, and thought leadership, building an ecosystem in which original thinkers, writers, and researchers are devalued while AI companies profit from their work.
The Effect on Organic Traffic for Bloggers and Businesses
Search engines have been the primary way website owners attract organic traffic and make ends meet. But with the introduction of AI search, that perfect economy is under attack.
When AI generates direct answers on the search results page, users no longer need to click on individual blog posts or websites. This dramatically reduces website traffic, making it harder for content creators to monetize their work through ads, affiliate links, or subscriptions.
A good example is Chegg’s 34% dip in organic traffic, which forced the educational tech company to sue Google.
While losing chunks of monthly visitors is a financial blow for Chegg and others in the same position, this shift is inevitable. People don’t need to scroll through multiple links and subsections to find answers. They’ve gotten the taste of the good life, and aren’t giving it up anytime soon.
As AI search engines refine their ability to generate responses, there’s a risk web users might continue to prioritize AI-generated summaries over original, human-written content.
This takes away ad revenue from bloggers and sales from businesses relying on organic visitors for conversions.
The Looming End of Free Search
What’s one advantage of AI? Well, no ads.
You no longer have to get constantly hijacked by ads and sponsored links screaming “Click here!” Just type in your question or prompt, and AI will supply straightforward responses instantly.
But here’s the catch:
AI-driven search engines require enormous computational power and data resources. According to the New York Times, Open AI lost roughly $5 billion to business expenses in 2026. To keep up with that cost, AI companies may eventually discontinue offering free searches and introduce fully paid models.
Some AI-powered search models like Perplexity and ChatGPT already charge for more advanced or personalized results at $35 and $20, respectively. With the continued dominance of AI, we could see tiered pricing models, where only the most basic searches remain free while deeper insights require a subscription.
Just as traditional search engines introduced paid ads, AI search could become increasingly biased toward sponsored results, where businesses must pay to appear in AI-generated answers. This could make it harder for smaller companies or independent creators to compete.
If AI becomes fully monetized, users may no longer find independent sources of information. Instead, search results could become dominated by large corporations that can afford to pay for visibility.
Will AI Kill Search? Here’s What You Can Do About It
No. AI won’t eliminate search, but it’s already affecting how we discover and consume information.
Instead of sifting through pages of search results, internet users now enjoy quick, AI-generated summaries. And search engines are getting better at understanding our needs and delivering more personalized results.
For website owners, SEO professionals, and marketers, this means staying ahead of the curve by publishing straightforward, people-friendly content to get ranked on AI’s responses.
Let’s take a look at what you can do to adapt to the new normal.
Shift Towards High-Quality, In-Depth Content
AI search engines like Perplexity AI and Google’s SGE don’t just scan for keywords. They analyze content semantically to determine its usefulness. This means surface-level or repetitive pieces will likely lose visibility, while well-researched and expert-driven articles will be rewarded with better rankings.
You can make your site a better contender by
-
Incorporating expert opinions and insights. AI models favor content that includes quotes, SME contributions, case studies, or original research over AI-generated texts or content spinning.
You can interview subject matter experts on platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Qwoted, and include their fresh angles into your content.
-
As a content marketer, you can also collaborate with data teams to create original, research-rich blog posts, as pages with unique insights will be favored over others.
For instance, rather than publish a generic piece about the “best SEO tips for 2026,” create a detailed guide with:
- Recent AI search updates
- Case studies from brands
- Actionable SEO techniques
- Expert insights from top marketers
Such content provides value beyond keyword targeting, making it more likely to get ranked, or featured in AI-driven search results.
Prioritize Conversational Writing
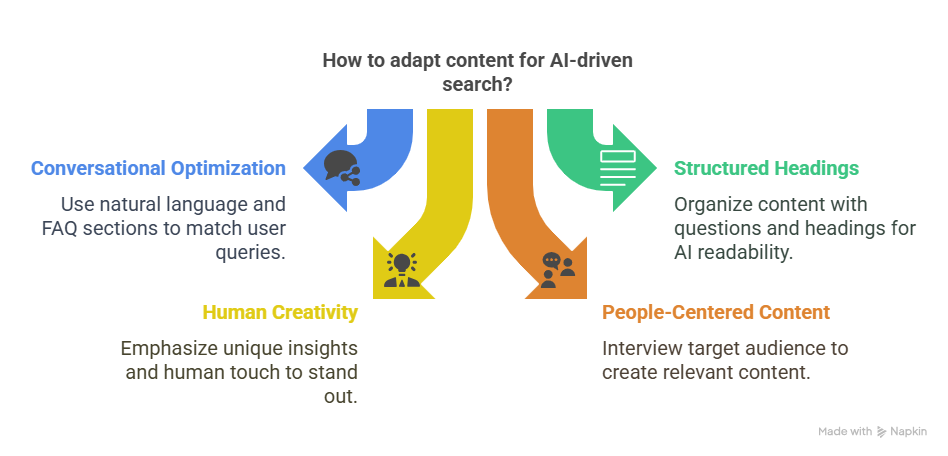
With AI processing natural language queries, users are shifting from typing short keywords to asking full, detailed questions and expecting natural answers.
To match this new user behavior, consider writing more casually. Substitute boring, business-speak for a conversational tone, like you’re chatting with a friend. Here are some tips to remember before you even start typing on Google Docs:
-
Optimize for conversational search: your content should reflect how real users ask questions. Use FAQ sections, dialogue-style writing, and natural phrasing.
-
Use structured headings and questions: AI pulls answers from well-formatted content. Structuring your articles with H2/H3 headings in a question-answer format improves ranking in AI-generated responses.
-
Uphold Human Creativity: As more AI-generated pieces circulate the web, search engines will reward human articles that provide unique angles, depth, and relevance. So, let your humanity shine in your writing. Abandon jargon and AI-generated fluff for fully human-written or humanized content.
If you’re using AI for your content creation, use it to generate a first draft but have an expert refine it with case studies, insights, and data while enhancing the flow with storytelling and a conversational charm.
-
Create People-Centered Content: When writing for a particular demographic, it makes sense to first interview at least two or more members of that group. This helps you understand their needs so you can create content they’ll find useful.
For instance, you can write a valuable piece about nursing mothers if you take the time to interact with them and discover what challenges they desperately want solved.
Invest in Multichannel Marketing
Sadly, even if AI links to your content, readers may not need to click through once they’ve digested the AI-summarized responses. This will lead to a drop in your monthly visitors, just like Cheggs and many businesses have experienced. But not everyone can afford to sue Google.
To supplement search engine traffic, businesses, and website owners should expand beyond SEO by investing in multichannel marketing to drive traffic to their site.
This will involve:
- Email marketing and newsletters: According to Litmus, you can expect an astounding $36 return on investment for every $1 spent on email marketing campaigns. So, if you haven’t already built your email list, it’s a good idea to start.
- Doubling down on social media content: Your LinkedIn, Twitter, YouTube, TikTok, and Pinterest accounts can be massive sources of inbound leads and organic visitors.
Pinterest alone has over 500 million active monthly users, making it a good option for businesses looking to drive website traffic and leads.
AI Is Here to Stay: Are You Ready?
AI-powered search is flipping the script on how we find information. It’s faster, smarter, and shockingly, more personal. But with this change comes a challenge: content creators can’t rely on old-school SEO tricks to stay visible. To track your visibility across AI platforms and understand how they mention and recommend your brand, tools like Nightwatch’s AI tracking can help you stay ahead.
To stand out, you’ll need more than surface-level content. Think depth. Think nuance. Create material so rich and original that AI can’t wrap it up in a neat one-sentence reply. It’ll just have to link back to it.
Search is evolving, and the ones who adapt will own the next era.
